BMS application state machine
This page will show the designed state machine and the description of the states from this state machine.
The main state machine
In Figure 2 the main state machine that will be implemented in the BMS can be found. This state diagram will be implemented in the BMS main loop.

Main state machine explained
SELF TEST state
The SELF TEST state is entered at power-up of the microcontroller. In this state the microcontroller initializes everything and performs the self-test, for example check if communication with a component is possible or check if the set output can be read. If everything is OK, it will go to the INIT state. If a watchdog reset has occurred not every self-test will be done to make sure the power is not turned off. The LED will be solid red in this state.
INIT state
The INIT state is typically entered from the SLEEP state. In this state the microcontroller unit (MCU) will wake up and it will verify configurations, fault registers and functions. This is needed because it can enter the INIT state when the user resets from a fault in one of the FAULT states as well. When everything is OK, it will close the power switch if not already closed and proceed to the next state depending on the current direction. The LED will be steady green in this state.
NORMAL state
This is the state where the battery operates how it should be, it is being discharged by the connected device, for example a drone. Meaning that the power switches are closed. The LED will be blinking green to indicate the state of charge. In this state the BMS performs the following tasks:
Battery voltage, cell voltage and current is measured and calculated every measurement cycle.
SoC and SoH are estimated every measurement cycle.
The DroneCAN/CyphalCAN BMS battery status will be send over the CAN bus every measurement cycle.
The user can read the BMS status and parameters with NFC and the CLI. The user may change the state to SLEEP.
A timer will monitor if the current is below the sleep current for more than the timeout period. If this happens, it will go to the SLEEP state.
It will monitor if the current flows in the battery and if the current is more than the sleep current for more than the charge detect time, the state will change to the CHARGE state.
If the current is less than the sleep current while the button is pressed for 5 seconds, it will transition to the SELF DISCHARGE state.
CHARGE state
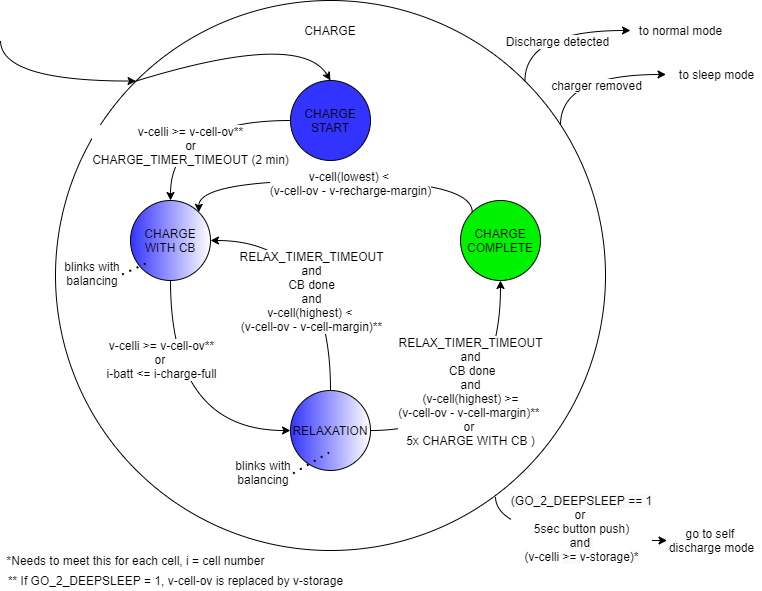
During this state the same functions as in the NORMAL state are implemented. The charging of the battery is done in different stages and is reflected in the charging state diagram in Figure 3. These are the states and their description:
CHARGE START: in this state the charging will begin, and a timer will start. The LED will be blue to indicate charging. After a set time (default 120sec) or if the voltage of one of the cells reaches the cell overvoltage level (to make sure there is no cell overvoltage error) the state will change to CHARGE WITH CB.
CHARGE WITH CB: in this state the cell balancing (CB) function will be activated. This function will calculate the estimated cell balance minutes per cell, which is based on the cell voltages, the difference compared to the lowest cell voltage, the balance resistor and the OCV-slope. The formula to calculate this estimated balance time is: Estimated balance minutes = (Vcell - Vcell_min ) * Rbal / (Vcell * ocvslope) Other than this calculated time, the BMS will check if the voltage of a cell that is being balanced, has reached the desired voltage as well. When the voltage of one of the cells reaches the cell overvoltage level or the charging current is less than the charge complete current, it will go to the RELAXATION state. The LED will stay blue and will blink if cell balancing is active. Balancing is finished if all the calculated cell balance minutes are expired or it has reached the lowest cell voltage.
RELAXATION: in this state the power switches are set open, disconnecting the charger from the battery. The MCU will be put in a very low power run (VLPR) mode (BMS application STANDBY mode), SBC in standby mode and the BCC to measure only at 10Hz. This will reduce the power in this state. The battery will relax for the specified relax time (default 300 sec). During this relaxing, the cells can still be balanced since this happens with a low balancing current. At the end of the relaxation period, the system will check whether the balancing is done. If balancing is not finished, the BMS will re-estimate the balance minutes. If balancing is finished and the highest cell voltage is lower than the cell overvoltage minus the voltage margin, it will return to the CHARGE WITH CB state to continue the charge process. If the highest cell is within this margin, the charging is complete, and it will go to the CHARGE COMPLETE state. To make sure it won’t endlessly go through this cycle with the CHARGE WITH CB state (this can happen if the end of charge current is met but the voltage requirement is not met), after 5 times it will just not check if the highest cell voltage is within this margin and will go to the CHARGE COMPLETE state
CHARGE COMPLETE: in this state, the charging is done, and the LED will be steady green. If the lowest cell voltage decreases again below the cell overvoltage minus the recharge voltage margin, it will go to the CHARGE WITH CB state again. The power switches will remain open and if the charger is disconnected it will go to the SLEEP state after the defined period of time.
If at any time the current flows from the battery to the output and this current is higher than the sleep current, the BMS transitions to the NORMAL mode. If a charger is disconnected, the state will transition to the SLEEP state. If the go to deep sleep command has been given or the button is pressed for five seconds there are two options: If one cell voltage is less than the storage voltage it will complete charging until each cell has reached the storage voltage, after this is done the BMS will transition to the SELF DISCHARGE state and this will then transition to the DEEP SLEEP state. The other option is that no cell voltage is less than the storage voltage, than the BMS will transition to the SELF DISCHARGE state.
SLEEP state
The sleep state is typically entered when the current is very low for an amount of time. This SLEEP state is used to preserve power. The MCU will be put in VLPR mode, the SBC in standby mode, the BCC in sleep mode with measurement on to check for a sleep overcurrent and other faults. This is the BMS application VLPR mode. The power switches will be closed to make sure the battery could be used. If any threshold is met during a cyclic measurement or the button is pressed, it will wake the MCU and the BMS will transition to the INIT state to check status. If the button is pressed for five seconds, the state will change to the SELF DISCHARGE state, in order to go to the DEEP SLEEP state. If the t-sleep-timeout happens the BMS will go to the SELF DISCHARGE state and will discharge the battery to storage level. After this it will go to the DEEP SLEEP state. In this state the LED will be off.
OCV state
The OCV state will allow to record the latest open cell voltage (OCV) of the battery which is used in the state of charge (SoC) computation. Cyclically the Battery will enter this mode when the Battery stays in the SLEEP state. The period the system will go from the SLEEP state to the OCV state will depend on the time since the battery has entered the SLEEP state in the first place, without going to another state except the OCV state. The time to enter the OCV state will gradually increase each time with 50% from the set begin time until the set end time is reached. If for example the set begin time is five minutes and the set end time is twenty-four hours, it will take fifteen times to have a period of is twenty-four hours. When entering this mode, the MCU will wake up the AFE and measure. After it has calibrated the SoC, it will go to the SLEEP state again. The LED will blink green in the OCV state.
FAULT_ON state
The FAULT_ON state is entered when a critical fault has been detected (over-current, over-voltage, cell over-temperature) and requires evaluating if the battery needs to disable the output power. In this state the power will remain ON. With the flight-mode-enable and the i-flight-mode parameter, the user can make sure that the battery will not be disconnected from the power out connector and the BMS will stay in this state. If the s-in-flight parameter is high, it will stay in this state and not disconnect the power. Except, when the i-peak-max threshold is reached.
The s-in-flight parameter is high if the i-batt-avg (1s) is higher than i-flight-mode and the i-batt-avg (1s) is less than the i-out-max AND the flight-mode-enable is high.
The s-in-flight will be low again when: the i-batt-10s-avg is lower than the i-flight-mode and the i-batt-avg (1s) is less than the i-flight-mode. OR s-in-flight will be low when the flight-mode-enable is set to 0 OR when there is a i-batt-avg (1s) charge current higher than the i-sleep-oc ((1s_current_avg - i-sleep-oc) > 0). If the BMS is in the FAULT_ON state and s-in-flight will become false, it will go to the FAULT_OFF state.
If the BMS needs to turn off the power, it will go to the FAULT_OFF mode. Other ways to exit this FAULT_ON state is that the user can manually force the BMS to go to the INIT state via the reset fault command with the CLI or by activating the push button. If there is an undervoltage fault, it could transition to the DEEP SLEEP state after the t-fault-timeout time. In this state the LED will be solid RED to indicate the power is still on.
FAULT_OFF state
The FAULT_OFF state is entered when there is a fault and it needs to turn off the output power. In this state the power will be turned OFF. Usually, this state is entered because in the FAULT_ON state it noticed that it needs to turn off the power. It will go directly in the FAULT_OFF state if the emergency button is used and this button is active or if a hardware overcurrent is detected. To exit this FAULT_OFF state is that the user can manually force the BMS to go to the INIT state via the reset fault command with the CLI or by activating the push button. If there is an undervoltage fault, it could transition to the DEEP SLEEP state after the t-fault-timeout time. In this state the LED will be blinking RED to indicate the power is off.
SELF DISCHARGE state
This state is used to discharge the cells to the cell storage voltage in order to improve its life duration, when storing the battery for long time. In this mode, the power switches are open, the MCU is powered and the balancing functions are activated. When the storage voltage is reached for each cell or if cells have a lower voltage, it will transition to the DEEP SLEEP state. CAN communication is disabled. To get a better SoC estimation, the OCV is measured and this will update the SoC measurement of the battery. To exit this state and to go back to the INIT state, the button needs to be pressed. The LED will blink blue in this state
DEEP SLEEP state
This state is used for transportation and storage. In this state, the power switches are open, disconnecting the battery, all protections are turned off, there are no cyclic measurements done, the LED is off, and it will set everything to sleep or off to ensure the lowest power usage (<100uA). Only the button can wake everything in this state. When the button is pressed, it will transition to the SELF_TEST state. When entering this mode, the MCU will check if at least one configuration parameter has changed. If configuration parameters have changed, it will save the parameters to flash to make sure they are loaded at startup. The LED will be white for 1 second before going off for the rest of the time in this state.
Last updated